
Discover More
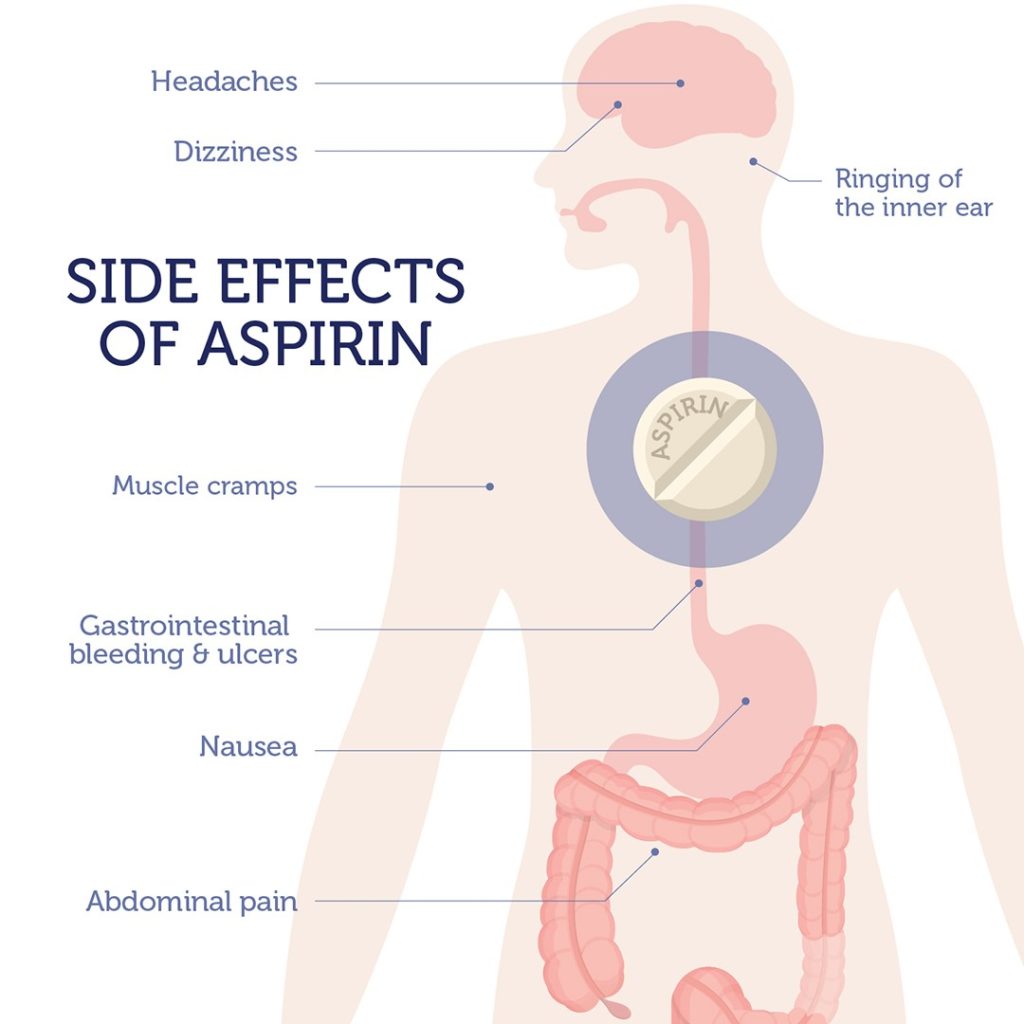
Potential side effects of aspirin:
- Gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers
- Ringing of the inner ear
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Headaches
- Muscle cramps
INCREASED risk of colorectal cancer if you have inherited the “wrong” genes
Trending Now
$149.00
By Genovate
Has your doctor recommended regular low-dose aspirin to prevent colorectal cancer? Did you know the benefits of aspirin actually depend on your genes? Find out if aspirin is the best treatment for you.
• Detects changes in MGST1 and IL6 genes linked to colorectal cancer risk
• People with the rare MGST1 variant increase their risk of cancer by taking aspirin
• Those with the IL6 variant do not benefit from aspirin
Aspirin reduces inflammation and inhibits blood clots by blocking the action of an enzyme called cyclooxygenase. Aspirin is widely recommended for at-risk individuals to help prevent heart attacks.
Several studies have also identified an association between aspirin use and a reduced risk of developing colorectal cancer.
BUT, not everyone receives the same benefit from aspirin use. Some people inherit genetic variants that actually increase their risk of colorectal cancer if they take aspirin regularly.
Take this DNA test to see whether aspirin is the best preventative method for you.
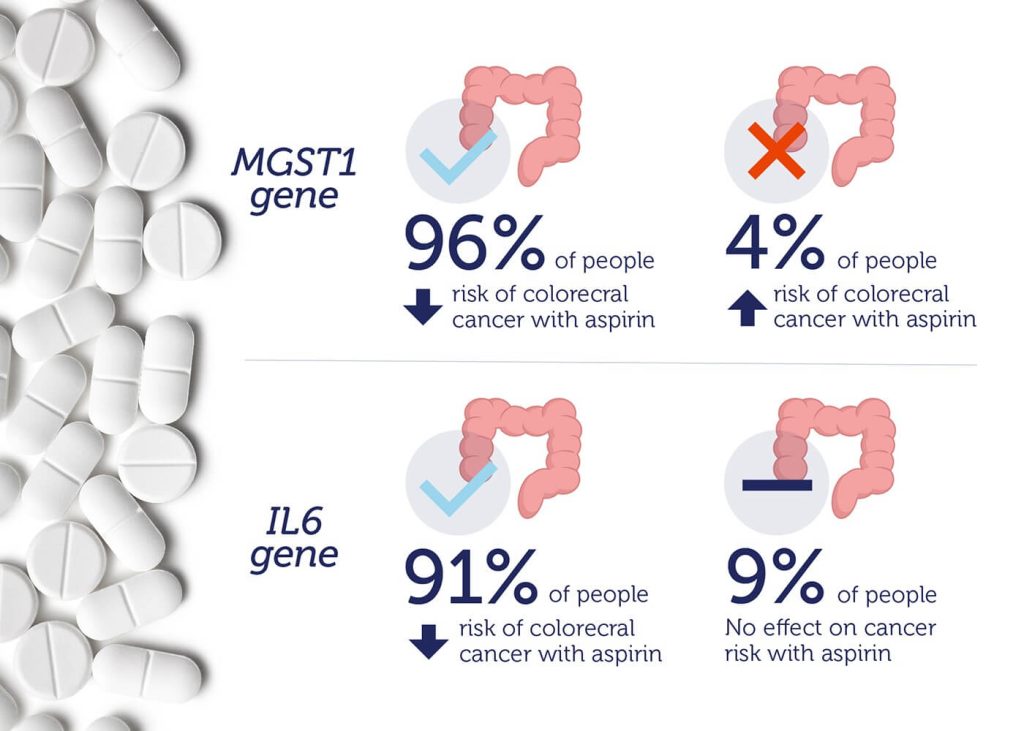
A recent study has shown that two genetic variants can influence the link between aspirin and colorectal cancer risk. The most common nucleotides at rs2965667 near the MGST1 gene, and rs16973225 near the IL16 gene are associated with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer if aspirin is used regularly.
But, people who inherit the rare “wrong” alleles don’t receive colorectal cancer-related benefits from aspirin use:
Potential side effects of aspirin:
INCREASED risk of colorectal cancer if you have inherited the “wrong” genes


© DNA in the News